Cyber security and AI
Cybersecurity and AI
04.07.2024.

Cybersecurity and AI
Over the past few years, we have witnessed increasing advancements and applied uses of AI, from business to various private purposes, thereby opening up even greater space for various vulnerabilities and challenges that AI brings with it.
The interdependence of AI and cybersecurity, although multidimensional, can be viewed from two directions/focuses:
- cybersecurity of artificial intelligence and
- artificial intelligence in cybersecurity.
Figure 1. Interconnection of artificial intelligence and cybersecurity
Cybersecurity of artificial Intelligence
This primarily refers to the requirements of the EU Artificial Intelligence Act regarding cybersecurity. Suppliers of high-risk AI systems will need to achieve a certain level of compliance prescribed by the requirements of the Act, with cybersecurity standards playing a key role.
Cybersecurity is key for the resilience of AI systems
Article 15 states: „high-risk AI systems shall be designed and developed in such a way that they achieve an appropriate level of accuracy, robustness, and cybersecurity”. Additionally, Recital 51 states that cybersecurity is crucial for the resilience of AI systems against attempts by malicious third parties exploiting system vulnerabilities to alter their usage, behavior, capacity, or to compromise their security mechanisms. Cyber attacks on AI systems can exploit unique AI resources, such as data sets for learning (e.g., data poisoning) or trained models (e.g., adversarial attacks), or exploit weaknesses in the digital resources of AI systems or the underlying ICT infrastructure.
To ensure a level of cybersecurity that matches the risks, suppliers of high-risk AI systems should take appropriate measures, considering the underlying ICT infrastructure as needed.
Thus, high-risk AI systems must meet cybersecurity requirements before being used in the EU market, and AI system suppliers must ensure cybersecurity and its updates throughout the life cycle of the AI system.
Cybersecurity requirements for high-risk AI systems
The report “Cybersecurity of Artificial Intelligence in the Artificial Intelligence Act” focuses on the cybersecurity requirements for high-risk AI systems, as specified in Article 15 of the Act. It defines the term “AI cybersecurity” as an emerging field of study that gathers and combines knowledge and approaches from various areas such as artificial intelligence research, adversarial/hostile machine learning, and general cybersecurity.
Challenges of artificial intelligence cybersecurity can be divided into two categorie:
- organizational challenges related to processes and
- research and development challenges related to techniques and technology.
There are four main principles for addressing the requirements of the Artificial Intelligence Act in terms of cybersecurity:
- the focus of the Artificial Intelligence Act is on AI systems;
- compliance with the Act necessarily requires a security risk assessment;
- protection of AI systems requires an integrated and continuous approach using proven practices and controls specific to AI;
- there are limitations of cutting-edge technologies in protecting AI models.
In the years ahead, cybersecurity of artificial intelligence will become increasingly important, and it could be said, a critical area. Companies involved in cybersecurity will have increased demands for implementing their services, standards, and solutions primarily in high-risk AI systems.
Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity
Here we look at cybersecurity threats using artificial intelligence, as well as the potential of artificial intelligence in defending against cyber incidents. Some of the key benefits of using artificial intelligence in cybersecurity (defense) include:
- DATA PROTECTION IN HYBRID ENVIRONMENTS (CLOUD).
AI solutions can identify “shadow data,” track abnormalities/anomalies in data access, and alert cybersecurity experts to potential threats from anyone accessing data or sensitive information. They also save valuable time in detecting and resolving issues in real time.
- GENERATING MORE ACCURATE AND PRIORITIZED THREATS.
Risk analysis driven by AI can produce incident summaries for high-accuracy alerts and automate incident responses, speeding up alert investigations and triage by an average of 55%. AI technology also helps in identifying vulnerabilities and defending against cyber criminals and cybercrime.
- ALIGNING USER ACCESS NEEDS WITH SECURITY.
AI models can help find a balance between security and user experience by analyzing the risk of each login attempt and verifying users through behavioral data (behavioral analysis), simplifying access for verified users and reducing fraud costs by up to 90%. AI systems also help prevent identity theft, malware, and other malicious activities, ensuring a high level of security.
HIGHLIGHTED STATISTICS:
Organizations with fully implemented AI security systems have on average reduced data breach costs by USD 3 million. These capabilities also contribute to time savings. For example, the required time from 230 days (for detection, response, and recovery) is reduced to 99 days, and organizations with the most mature AI systems and automation capabilities achieve a
40% higher Return on Security Investment (ROSI).
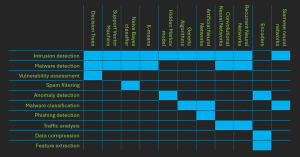
The table shows AI methods in the function/s of cybersecurity (ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND CYBERSECURITY RESEARCH; ENISA Research and Innovation Brief; JUNE 2023)
The trend of increasing AI usage in cybersecurity continues
The use of generative artificial intelligence for cybersecurity purposes is rapidly increasing and will continue to grow. Companies will increasingly consider the AI capabilities of systems when selecting cybersecurity systems (e.g., SOC, SIEM, etc.).
Threats to cybersecurity using artificial intelligence are causing increasing concern among organizations and individuals, as they can bypass traditional security measures and cause significant damage.
Some of the threats that require special attention include (a summarized list):
- the use of artificial intelligence by APTs (Advanced Persistent Threats) to avoid detection during attacks on specific organizations or individuals;
- malicious code powered by artificial intelligence (AI-powered malware);
- automated exploitation of vulnerabilities;
- credential stuffing attacks; and
- Automated botnets.
If you are subject to NIS2 and DORA, and you use AI in your operations, you face an additional challenge related to identifying and mitigating risks arising from the use of such new technology. AI systems, like all others used in the organization, must comply with applicable legal frameworks.
Check out how Diverto approaches achieving compliance, as well as a high level of security, and how we can help you achieve your security goals.
MORE